A JavaScript variable is simply a container for a value that can be changed later on.
In JavaScript, we declare a variable and we do so with the use of keywords var, let and const .
Let's discuss each of the keywords.
1. let keyword :
The let keyword allows you to declare variables that are limited to the scope of a block statement, or expression on which it is used. It cannot redeclare a variable.
2. var keyword :
The var keyword allows you to declare a variable globally, or locally to an entire function regardless of block scope. We can redeclare a variable with the use of the var keyword.
3. const keyword :
The const keyword creates block-scoped constants, much like variables declared using the let keyword. The value of a constant can't be changed through reassignment and it can't be redeclared.
Note : let and const are both relatively new ways to declare variables in JavaScript.
Declaring a JavaScript Variable
Creating a variable in JavaScript is called "declaring" a variable.
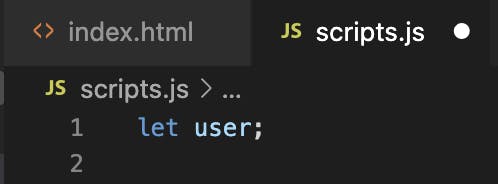
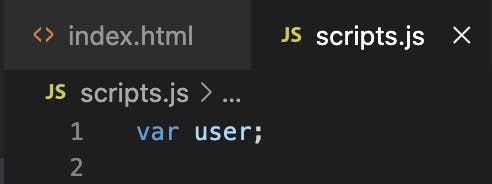
Assigning Values To JavaScript Variable
After the declaration, the variable has no value
(technically it is undefined).
To assign a value to the variable, use the equal sign '='.
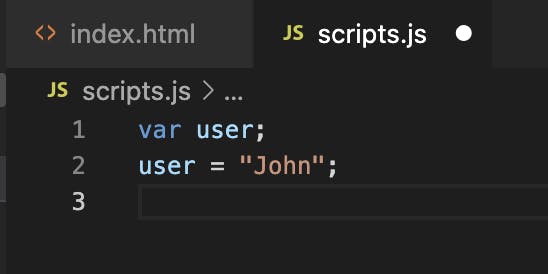

Naming Of JavaScript Variables
The general rules for constructing names for variables (unique identifiers) are:
Names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
Names must begin with a letter.
Names can also begin with $ and _.
Names are case-sensitive.
Reserved words (like JavaScript keywords) cannot be used as names.
Note :
Difference between
letkeyword andvarkeyword.In most cases
varandletbehave the same way, but sometimes the behaviour ofvaris not what you would expect.varvariables have no block scope, their visibility is scoped to the current function, or global if declared outside the function.vardeclarations are processed at function start (script start for globals).
If you liked this article, consider following me on Hashnode for my latest publications.
